Issue No. 137
Summarised from Journal of Clinical Periodontology, Volume 52, Issue 5, May 2025, 666–680
Editor: James Deschner, chair, EFP scientific affairs committee
How effective is systemic azithromycin as adjunct to non-surgical subgingival instrumentation?
Authors: Srinivas Sulugodu Ramachandra, Valerie Woodford, Pingping Han, Ryan S. B. Lee, Sašo Ivanovski
Background
Periodontitis, as a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the supporting structures of teeth, requires mechanical subgingival instrumentation (SI) as cause-related therapy. This study investigated the potential benefits of systemic delivery of azithromycin as an adjunct to non-surgical subgingival instrumentation (NSI) in the treatment of stage III/IV, grade C periodontitis. Azithromycin is known for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a potential adjunctive antimicrobial agent during NSI.
Aim
To evaluate the clinical, microbial, and cytokine changes over 12 months following delivery of systemic azithromycin, adjunctive to NSI, in stage III/IV, grade C periodontitis through a triple-blind, parallel-armed, randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Materials and methods
- Study design: Triple-blind, parallel-arm, placebo-controlled RCT conducted from March 2019 to August 2022.
- Patient cohort: 52 patients diagnosed with stage III/IV grade C periodontitis were randomly allocated to two groups receiving NSI with or without adjunctive systemic azithromycin.
- Interventions:
- NSI was performed under local anaesthesia, followed by oral-hygiene instructions and reinforcement.
- Patients received either azithromycin or placebo capsules, administered once daily for three days starting immediately before NSI.
- Outcome measures:
- The primary outcome was the change in periodontal inflamed surface area (PISA) values over 12 months.
- Secondary outcomes included changes in probing depth (PD), clinical attachment level (CAL), bleeding on probing (BoP), percentage of sites with PD of 1–3, 4–5, ≥5, and ≥6mm, subgingival periodontal pathogens, cytokine levels, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs).
- Statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney and Friedman’s tests were applied for intergroup comparisons and timepoints. Two-way ANOVA was used for patient-reported outcomes.
Results
- Patient profiles: The mean age of patients was 58.3 ± 10.8 years in the placebo group and 50.92 ± 11.37 years in the azithromycin group, respectively. Both groups displayed comparable male-to-female ratios and ethnic distributions. Established disease modifiers included smoking and diabetes mellitus.
- Primary outcome: At three and 12 months, there were no statistically significant differences in the reduction in PISA between the groups. The mean reduction for PISA scores was 1329.9 ± 732.6mm² in the azithromycin group and 1081.0 ± 529.2mm² in the placebo group at three months, and 1348 ± 691.7mm² in the azithromycin group and 1163.0 ± 574.7 mm² in the placebo group at 12 months.
- Secondary outcomes:
- Clinical findings: No statistically significant differences were observed in clinical parameters such as mean PD, mean CAL, and BoP (%) between the groups at three and 12 months. The percentage of sites with PD ≥5mm was statistically significantly smaller in the azithromycin group compared to the placebo group at 12 months, while the percentage of sites with PD ≥6mm was statistically significantly smaller in the azithromycin group compared to the placebo group at three months.
- Microbiological findings: At three months, significantly lower levels of several periodontal pathogens—including T. forsythia, T. denticola, P. intermedia, E. corrodens, and P. anaerobius—were observed in the azithromycin group compared to the placebo group. At 12 months, no statistically significant differences between the groups were observed for the studied bacteria except for P. intermedia.
- Cytokine findings: No statistically significant differences between groups for the studied cytokines were observed. The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 showed variations over time but did not differ statistically significantly between groups.
- Patient-reported outcomes (PROs): High levels of patient satisfaction were reported in both groups. Reductions in pain and discomfort, dental hypersensitivity, and healthier gums following treatment were reported. Patients expressed willingness to undergo the same treatment again and indicated that their expectations had been met.
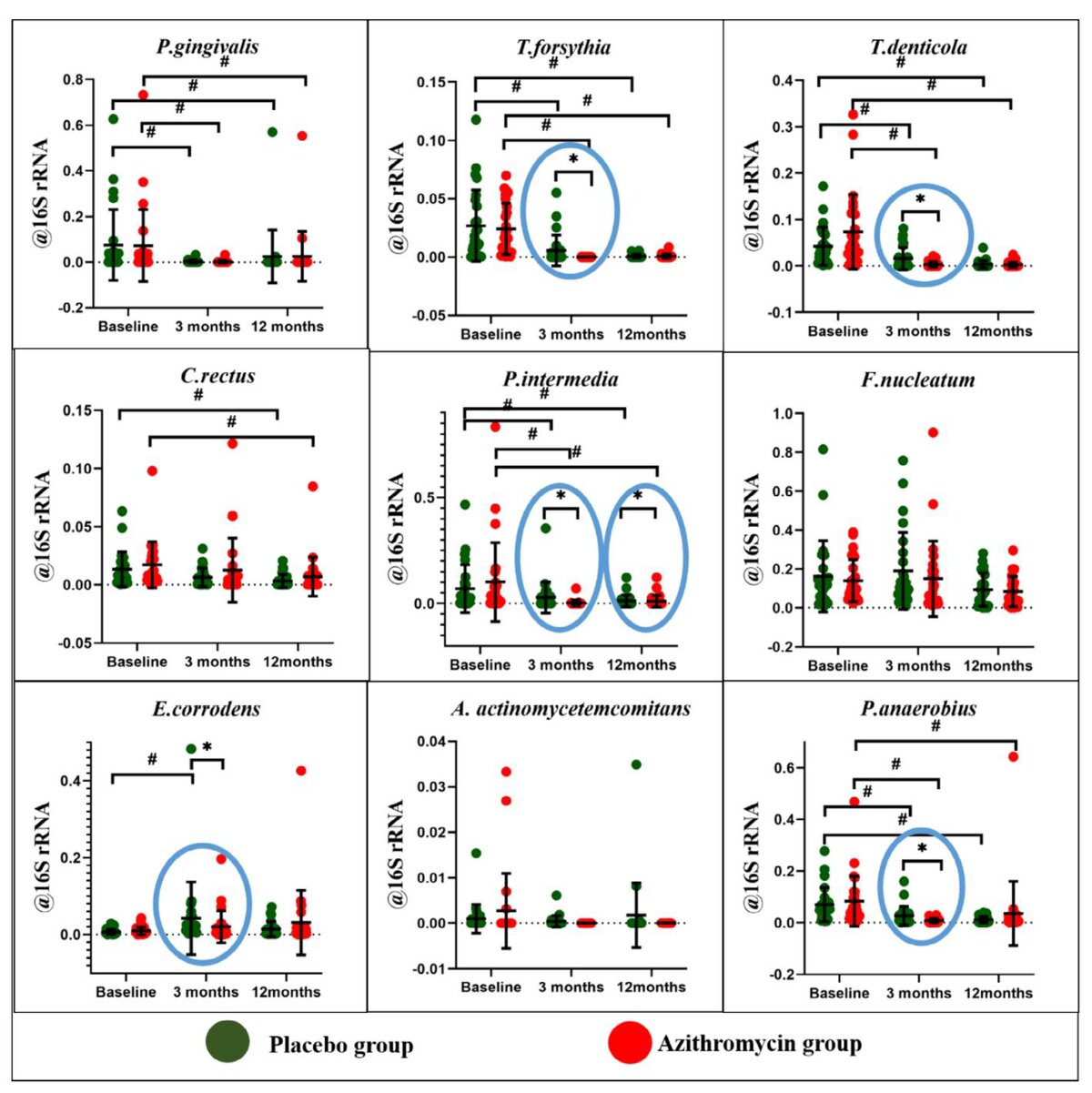
* Significant difference between placebo and azithromycin groups; # significant difference between baseline, three months and 12 months. The blue circle highlights the data with significant difference between groups.
Limitations
- No specific threshold of full-mouth plaque score was considered as an inclusion criterion.
- A limited number of periodontal pathogens and cytokines were assessed.
- No separate sub-analysis of disease modifiers such as smoking and diabetes mellitus was performed because of the small sample size.
Conclusions and impact
- Systemic azithromycin as an adjunct to NSI failed to yield significant reductions in PISA scores at 12 months in stage III/IV, grade C periodontitis patients.
- A short-term reduction in periodontal pathogens was observed, but no significant differences—with the exception of P. intermedia— were found at 12 months.
- The outcomes of the study suggest that while adjunctive azithromycin may have short-term anti-microbial effects, its benefits are not sustained at 12 months.
The study does not support the adjunctive use of systemic azithromycin in stage III/IV, grade C periodontitis. The findings highlight the need for careful consideration of adjunctive antibiotic therapies in periodontitis patients, aligning with public-health recommendations to limit unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions. This is also in accordance with the suggested use of systemically administered antibiotics in the EFP S3-level clinical practice guideline on the treatment of stage I–III periodontitis.
Rapporteur: Jan Schmid, supervised by Prof. Giovanni E. Salvi.
Affiliation: Postgraduate programme in periodontology, University of Bern, Switzerland.
With kind permission from Wiley Online Library. Copyright © 1999-2025 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved